Anterior horn cell disease pdf
Madras Motor Neuron Disease (MMND), also referred to as Madras pattern motor neuron disease, is a rare young age onset progressive neuro muscular disease taking relatively benign course. MMND has predominant geographic distribution in southern India.
Motor Neuron Disease • Incidence: 2-4 per 100 000 • Onset: usually 50-70 years • Pathology: –Degenerative condition –anterior horn cells and upper
Abstract. The lethal congenital contracture syndrome (LCCS) is an autosomal recessive syndrome (McKusick 253310) leading to perinatal death owing to early onset degeneration of the anterior horn motor neurones of the spinal cord.
Sutay et al; Anterior Horn Cell Disease Annals of International Medical and Dental Research, Vol (3), Issue (3) Page 27 Section: Paediatrics predilection also depends upon the type of disorder
335.0-335.21 Werdnig-Hoffman disease- progressive muscular atrophy 335.23-335.9 Pseudobulbar palsy- anterior horn cell disease unspecified 336.0-336.3 Syringomyelia and syringobulbia- myelopathy in other diseases
red blood cells by subtracting 1 white blood cell for every 500 red blood cells present [fungal meningitis case definition, CDC]). * Terms in the spinal cord MRI report such as “affecting mostly gray matter,” “affecting the anterior horn or anterior horn cells,”
Direct viral damage to anterior Immune-mediated damage to peripheral horn cells (e.g.polio) nerves (e.g.Guillain–Barré syndrome) Paralysis onset During (or straight after) Several weeks after febrile illness
Chan LG, Parashar UD, Lye MS, et al. Deaths of children during an outbreak of hand, foot, and mouth disease in sarawak, malaysia: clinical and pathological characteristics of the disease. For the Outbreak Study Group. Clin Infect Dis 2000; 31:678.
Mutations in GLE1 underlie Lethal Congenital Contracture syndrome (LCCS1) and Lethal Arthrogryposis with Anterior Horn Cell Disease (LAAHD). Both LCCS1 and LAAHD are characterized by reduced fetal movements, congenital contractures, and a severe form of motor neuron disease that results in fetal death or death in the perinatal period, respectively.
28/04/2014 · In the LMN system, there is loss or degeneration of the anterior horn cells (especially the large neurons) with anterior nerve root atrophy, as well as of the brainstem motor nuclei (eg, cranial nerve [CN] XII, motor VII, and motor V) (see the images below).
Australian Paediatric Surveillance Unit STUDY PROTOCOL Commenced 1995 Revised AFP Study Acute Flaccid Paralysis Protocol 06/2014 The AFP Study Group announces a briefer questionnaire for the collection of clinical data.
1/04/2011 · We concluded that this was an acquired, non-progressive anterior horn cell disorder that represented a benign variant of the progressive muscular atrophy form of motor neuron disease. The somewhat ill-defined clinical syndrome of cramp-FS without myokymia or …
89 Spinal cord Weakness Weakness; Myopathy, Anterior horn cell disease, Neuropathies and Neuromuscular transmission defects In the neurological evaluation of weakness, we distinguish between upper motor neuron
Synonyms: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Lou Gehrig’s disease (USA form – named for a famous baseball player who succumbed to the disease), Charcot’s disease, Charcot’s syndrome, Charcot’s sclerosis Motor neurone disease (MND) is a rare but devastating illness which leads to progressive
The hallmark of WNV encephalitis is the combination of encephalopathy with lower motor neuron dysfunction owing to anterior horn cell disease or motor axonal neuropathy, or both. Pathological study of autopsy cases 23 , 24 and experimentally infected monkeys 21 suggests that inflammation in the anterior horns of the spinal cord, 21 , 23 , 24 with motor neuron dropout, is the cause of the
20/09/2011 · In addition, note the linear T2 intramedullary hyperintensity, representing atrophy and gliosis of the anterior horn cells (large arrow). (B) Transverse T2-weighted image demonstrating the owl eyes sign (hyperintensities in the anterior horns of gray matter), representing atrophy and gliosis of the anterior horn cells (white arrows).
The anterior horn cells are located in the gray matter of the spinal cord and thus are technically part of the CNS. In contrast to the motor system, the cell bodies of the afferent sensory fibers lie outside the spinal cord, in dorsal root ganglia.
Poliovirus has a predilection for the motor neurons of the anterior horn of the cervical and lumbar regions of the spinal cord, which can result in the cell death or injury of these motor neurons. Following death of the anterior horn cells, wallerian degeneration results and the muscle fibres
CHAPTER 34
C5 palsy following ACDF aanos.org
Anterior horn cell disease in England 1996 to 2004. Mortality trends Authors: Michael Goldacre, Marie Duncan, Paula Cook-Mozaffari, Matthew Davidson, Henry McGuiness, Daniel Meddings Published by: Unit of Health-Care Epidemiology, Oxford University, and South-East England Public Health Observatory, 2006 This document provides a profile of trends in mortality for anterior horn cell disease …
Anterior horn cell disease Motor neuron pathology. • Vulnerable to defects in excitotoxicity, RNA transport and splicing,axonal protein transport, mitochondrial function,protein
• Anterior Horn Cell Disease (SMA) (335.0-335.21) • Other Motor Neuron Disease (335.23-335.9) • Other Diseases of the Spinal Cord (336.0-336.3) • Multiple Sclerosis (340) • Other Demyelinating Diseases of CNS (341.0-341.9) • Hemiplegia and Hemiparesis (342.00-342.92) • Infantile Cerebral Palsy (343.0-343.9) • Quadriplegia, Quadriparesis, Paraplegia (Lower Limbs) (344.00-344.1
Terms in the spinal cord MRI report such as “affecting mostly gray matter,” “affecting the anterior horn or anterior horn cells,” “affecting the central cord,” “anterior myelitis,” or “poliomyelitis” would all be consistent with this terminology.
In the progression of the disease there is a loss of motor neurones from the anterior horn of the spinal cord, the primary motor cortex and from the hypoglossal nucleus in the lower medulla. Surrounding glial cells are also affected. Shrinkage and discolouration of the anterior nerve roots in the spinal cord occurs because of axonal degeneration of the neurones and the accompanying demyelination.
This page was last edited on 12 September 2018, at 20:30. All structured data from the main, property and lexeme namespaces is available under the Creative Commons CC0 License; text in the other namespaces is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; …
Electrophysiologic Evidence for Anterior Horn Cell Disease in Amyoplasia John N. Gaitanis, MD*, Hugh J. McMillan, MD, MSc†, Allan Wu, MD‡, and Basil T. Darras, MD†
Acute Non-Traumatic Weakness: 7 Anatomical Localization Based on the location of nervous system pathology Understanding the cause of weakness can be aided by localizing anatomically, since diseases
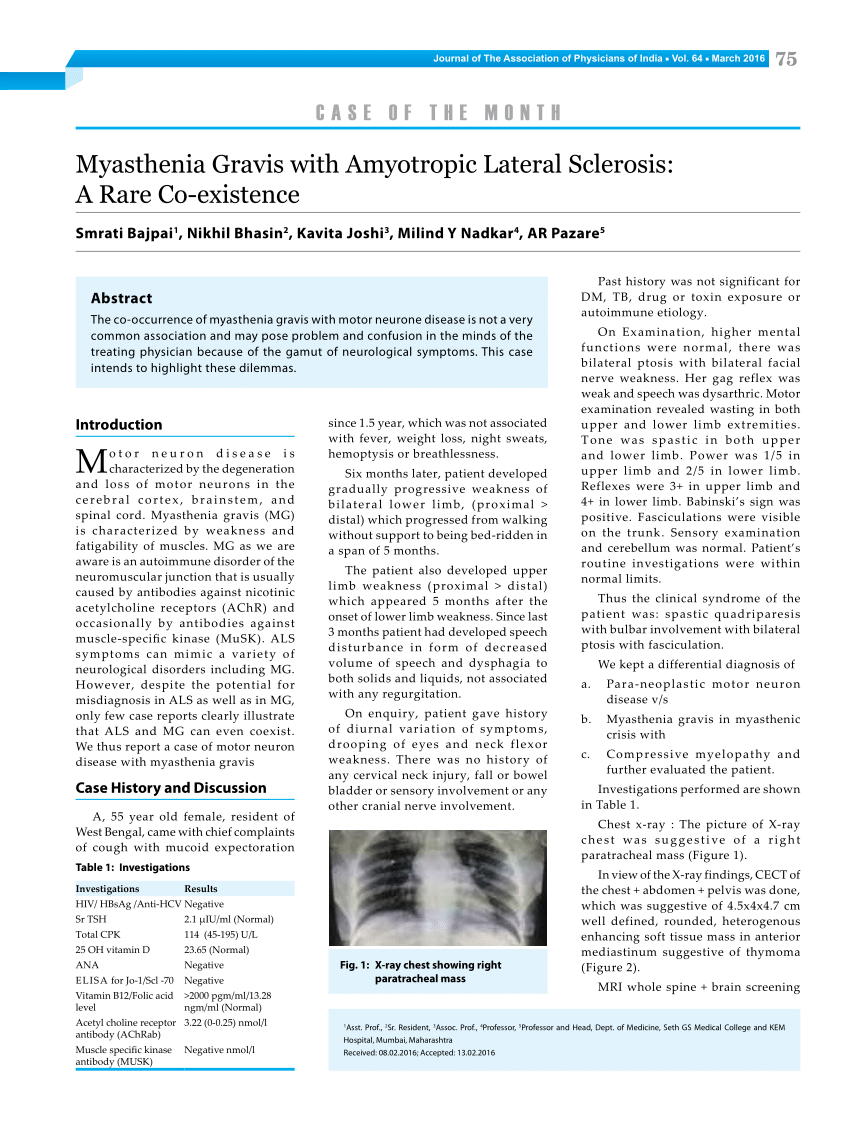
Get PDF (129K) Get PDF (129K) The following case reports describe a new condition of cerebellar ataxia, anterior horn cell disease, dystonia, and learning difficulties. Four cases are described.
30/11/2015 · (anterior horn cell) within the gray matter of the spinal cord (the part containing nerve cells), the nerve roots, the peripheral motor nerve, the neuromuscular junction, and …
Anterior horn cell disease was of a type not previously described at this age in association with cerebellar ataxia. Further genetic studies suggest the condition is not allelic with spinal muscular atrophy having no evidence of deletion of the survival motor neurone gene.
Causes of AFP Peripheral neuropathy Guillain-Barre syndrome Acute axonal neuropathy Neuropathies of infectious diseases Anterior horn cell disease
† Terms in the spinal cord MRI report such as “affecting mostly gray matter,” “affecting the anterior horn or anterior horn cells,” “affecting the central cord,” “anterior myelitis,” or “poliomyelitis” would all be consistent with this terminology.
Anterior Horn Cell Disease: (see Motor Neuron Disease) Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy: (see Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic) Anterior Pituitary Hyposecretion Syndrome: (see Hypopituitarism)
the anterior horn cell to the muscle result in the so called ‘neuromuscular’ conditions (see diagram below). For example, primary disorders of the nerve are called
anterior horn cells or the ventral rami of C5 are disrupted from degenerative disease, trauma or herniated disc a C5 palsy of varying degrees may occur. The contribution from the C6 ventral rami is essentially negligible in
Cerebellar ataxia anterior horn cell disease learning
Poliomyelitis is an acute communicable disease of humans caused by a human enterovirus of the Picornaviridae occurs when the virus enters the central nervous system and replicates in anterior horn cells (motor neurons) of the spinal cord. When it multiplies in the nervous system, the virus can destroy nerve cells (motor neurons) which activate skeletal muscles. The affected muscles lose
• Anterior horn cell Polio, Spinal Muscular Atrophy • Root Guillain Barre Syndrome • Nerve Bell’s Palsy, Polio, SMA, Hereditary Sensori‐Motor Neuropathy
Skein-like inclusions (SLIs) in the anterior horn cells of patients with motor neuron diseases, including familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with posterior column degeneration, sporadic lower
In addition, note the linear T2 intramedullary hyperintensity, representing atrophy and gliosis of the anterior horn cells (large arrow). (B) Transverse T2-weighted image demonstrating the owl eyes sign (hyperintensities in the anterior horns of gray matter), representing atrophy and gliosis of the anterior horn cells (white arrows).
In terms of the totality of disease, anterior horn cell disease is rare. Even in neurological practice spinal muscular atrophy is an uncommon condition. Motor neurone disease (MND) is the most common of the motor system diseases and, arguably, one of the most unpleasant diseases known to medical
aneurysm), tetanus, acute anterior horn cell disease, extensive denervation of skeletal muscle due to disease or injury of the CNS, or who have degenerative neuromuscular disease and …
Teaching NeuroImages: Anterior horn cell hyperintensity in Hirayama disease Jamsheed A. Desai, MD, BSc Michel Melanson, MD, FRCPC A 21-year-old man presented with gradually progres- – contouring tutorial with powder Anterior Horn. Anterior horns are the ventral extensions of the H-shaped gray matter and contain the large anterior horn cells (lower motor neurons) and smaller …
Full text Full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article (561K), or click on a page image below to browse page by page.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), commonly called Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a progressive neuromuscular condition characterized by weakness, muscle wasting, fasciculations and …
22/06/2018 · Acute poliomyelitis is a disease of the anterior horn motor neurons of the spinal cord and brain stem caused by poliovirus. Flaccid asymmetric weakness and muscle atrophy are the hallmarks of its clinical manifestations, due to loss of motor neurons and denervation of their associated skeletal muscles.
Expression of hepatocyte growth factor and c-Met in the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord in the patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): immunohistochemical studies on sporadic ALS and familial ALS with superoxide dismutase 1 gene mutation.
involvement of spinal anterior horn cells, resulting in a poliomyelitis-like syndrome. In areas in which transmission is occurring, WNV infection should be considered in patients with acute flaccid paralysis. Recognition that such weakness may be of spinal origin may prevent inappropri-ate treatment and diagnostic testing. Most human infections with West Nile virus (WNV), a flavivirus within
JournalofNeurology, Neurosurgery, andPsychiatry, 1977,40, 370-378 Anteriorhorncell disease associated with pontocerebellar hypoplasia in infants FRANCOISEGOUTIERES,JEANAICARDI, ANDEDITHFARKAS
II.Lesions of Anterior Horn cells at T1 level; Motor neuron disease Syringomyelia Polio.. Spinal muscular atrophy Peroneal muscular atrophy. Motor neurone disease: 1. No sensory signs 2. Fasciculations prominent; 3. wasted fibrillatory tongue . 4. Combination of UMN and LMN lesion 5. Hyper active reflexes despite wasting and fasciculation in the same muscles. Syringomyelia: Sensory
Acute flaccid paralysis (AFP) is a clinical syndrome which has many infectious and non-infectious causes. Causes of AFP are listed in Table 1 below. Causes of AFP are listed in Table 1 below. Notification Criteria
To date, fewer than 30 cases of anterior horn cell disease with associated olivopontocerebellar hypoplasia have been reported. We describe five patients and review the literature on this uncommon
Although polio no longer poses the worldwide public health threat that it once did, small areas of endemic wild-type poliovirus still exist in Asia and Africa. An understanding of this virus and other enteroviruses is important in the evaluation of the patient with acute flaccid paralysis. Human
Synaptic Alterations of Anterior Horn Cells in Werdnig-Hoffmann Disease Yoko Yamanouchi, MD*‘, Hideo Yamanouchi, MD*, and Laurence E. Becker, MD*
Lethal arthrogryposis with anterior horn cell disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner Lethal arthrogryposis with anterior horn cell disease (LAAHD) is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by reduced mobility of the foetus and early death.
2014 Reimbursement Guide 4 335.0-335.21 Werdnig-Hoffman disease- progressive muscular atrophy 335.23-335.9 Pseudobulbar palsy- anterior horn cell disease unspecified
1/22/10 8 Some Causes of Hypoventilation 1. Depression of the respiratory center by drugs (e.g., barbiturates) 2. Diseases of the medulla (e.g., encephalitis, hemorrhage, neoplasms [rare])
Abstract. Diseases affecting anterior horn cells may present at any age from infancy to the senium. Those diseases beginning in infancy, childhood or adolescence are usually limited to the anterior horn cells, but in adults other parts of the motor system, i.e. the upper motor neuron may be involved.
Anterior horn cells are also involved in Japanese encephalitis. Authors. U. K. Misra, Corresponding author. Department of Neurology, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow −226 014, India; Search for more papers by this author. J. Kalita. Department of Neurology, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow −226 014, India
gested a possible anterior horn cell disorder involving the C7–8 and T-1 segments of the cord. Plain cervical spine radiographs revealed no abnormalities except straight alignment. Nonflexion sagittal T1- and T2- weighted cervical MR images (1.5 T) showed equivocal cord atrophy in the lower cervical region without obvious canal stenosis (Fig 2A). The dura mater was in close contact with the
Skein-like inclusions in the anterior horn cells in motor
Neurological disorders of the shoulder:- how to recognise them and the role of the neurologist. Dr David Gow Consultant Neurologist Greater Manchester Neuroscience
CONDITION Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Anterior Horn Cell Disease Cerebellar Degeneration Primary Cerebral Palsy (CP) CNS Demyelination NEC
This observation does not invalidate the concept of functional groupings within these anterior horn cell pools In studies of the same segment in cords obtained at autopsy from patients with motor neuron disease, zones of focal loss of motor neurons were identified, without consistent severity or distribution at different sectional levels. These findings imply varying resistance to the disease
Causes of Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP1) Worldwide • Neuropathies of infectious diseases (diphtheria, Lyme disease) • Acute toxic neuropathies (heavy metals) • Arthropod bites • Focal mononeuropathy Anterior horn cell disease • Acute anterior poliomyelitis
Many anterior horn cell diseases cause arthrogryposis multiplex congenita, including spinal muscular atrophy , X-linked spinal muscular atrophy , lethal congenital contracture syndrome , Moebius syndrome , and pontocerebellar hypoplasia , . We can now add amyoplasia to the list of arthrogryposis syndromes that result from anterior horn cell lesions.
The diseases that damage anterior horn cells are generally more widespread and do not follow the distribution of a single nerve (although they can focus on one limb, especially early in the course). Neuromuscular disease .
Anterior horn cell disease associated with pontocerebellar

Teaching NeuroImages Anterior horn cell hyperintensity in
Australian Paediatric Surveillance Unit Annual Report, 2016 Marie Deverell, Amy Phu, Yvonne Zurynski, Elizabeth Elliott, and all chief investigators of APSU surveillance studies Abstract This report summarises the cases reported to the Australian Paediatric Surveillance Unit (APSU) of rare infectious diseases or rare complications of more common infectious diseases in children. During the
Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) is an idiopathic non-familial neurodegenerative disorder of upper motor neurons, presenting as a slowly progressive pyramidal tract syndrome. Disease onset is usually between
Autologous Bone Marrow Derived Stem Cells for Motor Neuron Disease with Anterior Horn Cell Involvement Introduction otor neuron disease (MND) is a
Anterior Horn Cell Syndrome Combined Anterior Horn cell Pyramidal Syndrome. Conus vs Cauda Conus medullaris lesion symmetric sensory/motor; bladder/bowel/sexual fxn early; sudden and bilateral Cauda equina lesion pain more prominent; gradual and unilateral. Infectious/Inflammatory Myelopathy Acute/subacute sx’s MRI: intramedullary lesions without evidence of extrinsic cord compression Sx
Anterior horn cell disease in England TrendsCover

Hirayama Disease MR Diagnosis AJNR
Acute Flaccid Paralysis Queensland Health


Australian Paediatric Surveillance Unit Annual Report 2016
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Grey_column
anterior horn cell disease Wikidata
– Synaptic Alterations of Anterior Horn Cells in Werdnig
Anterior spinal artery infarction causing man-in-the

Autologous Bone Marrow Derived Stem Cells for Motor Neuron
Acute Poliomyelitis Diseases & Conditions – Medscape
Hirayama Disease MR Diagnosis AJNR
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (aka ALS or Lou Gehrig’s
The anterior horn cells are located in the gray matter of the spinal cord and thus are technically part of the CNS. In contrast to the motor system, the cell bodies of the afferent sensory fibers lie outside the spinal cord, in dorsal root ganglia.
Australian Paediatric Surveillance Unit Annual Report, 2016 Marie Deverell, Amy Phu, Yvonne Zurynski, Elizabeth Elliott, and all chief investigators of APSU surveillance studies Abstract This report summarises the cases reported to the Australian Paediatric Surveillance Unit (APSU) of rare infectious diseases or rare complications of more common infectious diseases in children. During the
Abstract. Diseases affecting anterior horn cells may present at any age from infancy to the senium. Those diseases beginning in infancy, childhood or adolescence are usually limited to the anterior horn cells, but in adults other parts of the motor system, i.e. the upper motor neuron may be involved.
Abstract. The lethal congenital contracture syndrome (LCCS) is an autosomal recessive syndrome (McKusick 253310) leading to perinatal death owing to early onset degeneration of the anterior horn motor neurones of the spinal cord.
2014 Reimbursement Guide 4 335.0-335.21 Werdnig-Hoffman disease- progressive muscular atrophy 335.23-335.9 Pseudobulbar palsy- anterior horn cell disease unspecified
CONDITION Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Anterior Horn Cell Disease Cerebellar Degeneration Primary Cerebral Palsy (CP) CNS Demyelination NEC
Motor Neuron Disease • Incidence: 2-4 per 100 000 • Onset: usually 50-70 years • Pathology: –Degenerative condition –anterior horn cells and upper
Sutay et al; Anterior Horn Cell Disease Annals of International Medical and Dental Research, Vol (3), Issue (3) Page 27 Section: Paediatrics predilection also depends upon the type of disorder
1/22/10 8 Some Causes of Hypoventilation 1. Depression of the respiratory center by drugs (e.g., barbiturates) 2. Diseases of the medulla (e.g., encephalitis, hemorrhage, neoplasms [rare])
2014 Reimbursement Guide 4 335.0-335.21 Werdnig-Hoffman disease- progressive muscular atrophy 335.23-335.9 Pseudobulbar palsy- anterior horn cell disease unspecified
Anterior Horn Cell Diseases SpringerLink
C5 palsy following ACDF aanos.org
20/09/2011 · In addition, note the linear T2 intramedullary hyperintensity, representing atrophy and gliosis of the anterior horn cells (large arrow). (B) Transverse T2-weighted image demonstrating the owl eyes sign (hyperintensities in the anterior horns of gray matter), representing atrophy and gliosis of the anterior horn cells (white arrows).
Reimbursement Guide- Updated May 2013 VARILITE
Synaptic Alterations of Anterior Horn Cells in Werdnig
Skein-like inclusions in the anterior horn cells in motor
Anterior horn cell disease Motor neuron pathology. • Vulnerable to defects in excitotoxicity, RNA transport and splicing,axonal protein transport, mitochondrial function,protein
Acute anterior horn cell disease resembling poliomyelitis
Autologous Bone Marrow Derived Stem Cells for Motor Neuron
Causes of Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP1 Worldwide